
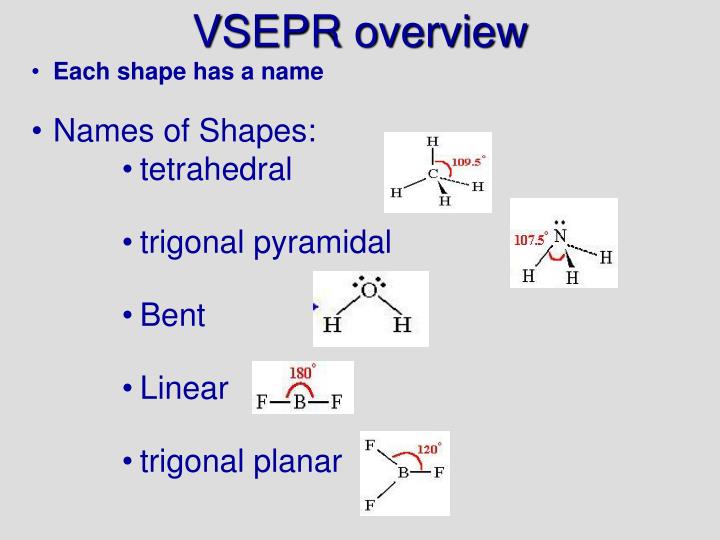
Dans ce cas, l'angle de liaison entre les deux atomes d'hydrogène est d'environ 104,45°. L'eau (H2O) est un exemple de molécule coudée, tout comme ses analogues. Certain atomes, tels que l'oxygène, ont presque toujours leurs deux (ou plus) liaisons covalentes dans des directions non colinéaires à leur configuration électronique. Cette géométrie s'appelle aussi parfois angulaire ou sous forme de V.

(See further discussion at VSEPR theory#Complexes with strong d-contribution). There exist also sd-hybridised AX2 compounds of transition metals without lone pairs: they have the central angle about 90° and are also classified as bent. AX2E1 molecules, such as SnCl2, have only one lone pair and the central angle about 120° (the centre and two vertices of an equilateral triangle). Other cases also experience orbital hybridisation, but in different degrees. The most common actual angles are 105°, 107°, and 109°: they vary because of the different properties of the peripheral atoms (X). They have central angles from 104° to 109.5°, where the latter is consistent with a simplistic theory which predicts the tetrahedral symmetry of four sp3 hybridised orbitals. There are several variants of bending, where the most common is AX2E2 where two covalent bonds and two lone pairs of the central atom (A) form a complete 8-electron shell. This geometry is almost always consistent with VSEPR theory, which usually explains non-collinearity of atoms with a presence of lone pairs.

Nonlinear geometry is commonly observed for other triatomic molecules and ions containing only main group elements, prominent examples being nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dichloride (SCl2), and methylene (CH2). The bond angle between the two hydrogen atoms is approximately 104.45°. Water (H2O) is an example of a bent molecule, as well as its analogues. Certain atoms, such as oxygen, will almost always set their two (or more) covalent bonds in non-collinear directions due to their electron configuration. In chemistry, molecules with a non-collinear arrangement of two adjacent bonds have bent molecular geometry, also known as angular or V-shaped.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
